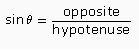Lesson 7: Introduction to Trigonometry
Created by IMSreader
Explore 2
The ratios that you calculated in the Discover section were ![]() ,
,![]() and
and ![]() .
.
These ratios have names.
-
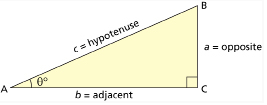
The sine ratio is the ratio of the length of the side opposite the reference angle to the length of the hypotenuse.
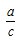
-
The cosine ratio is the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to the reference angle to the length of the hypotenuse.
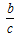
-
The tangent ratio is the ratio of the length of the side opposite the reference angle to the length of the side adjacent to the reference angle.
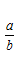
The definitions can be summarized by the following:
|
|
|
|
Notice that the ratios are based on the location of the reference angle.
A great way to remember the trigonometric ratios is by using the following:
SOH CAH TOA
If you chant SOH CAH TOA many times, the chant will stay in your head. (It sounds like “soak-a-toe-ah!”) Here’s what it means:
-------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Tip
Tip
For any calculations involving trigonometry, you must make sure that your calculator is in the “Degree” mode. Have a look at the calculator screen. Typically, calculators will show “Deg,” “Rad,” or “Grad.” You need your calculator to show “Deg.” If you see either “Rad” or “Grad,” you need to press the mode button until you see “Deg.”
If you cannot find the mode button, or if your calculator does not show any of the “Deg,” “Rad,” or “Grad” modes, then you can find out how to change the mode by reading in the calculator’s manual. These manuals can be searched on the Internet by typing your calculator’s make and model number into a search engine.
It is extremely important that you are in Degree mode. If not, your calculations will not be correct.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Learn and Listen
Watch this short video that shows how to find the sin, cos and tan of an angle given a triangle.
Here are some solved examples to study (all the sides are given so we do not have to use pythagorus)
1. Given the following triangles, state the sin, cos and tan for each of the acute angles in the triangle. ** Note - never find sin, cos and tan for the right angle**
a.
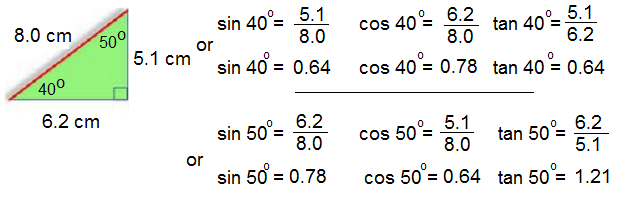
b. 
c.
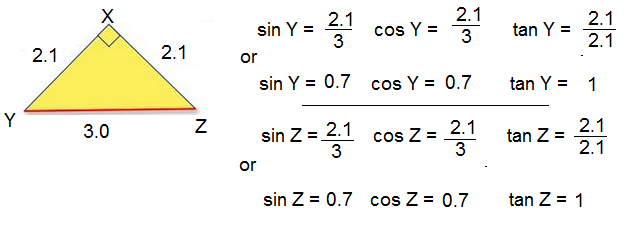
Learn and Listen
Watch this short video that shows how to find the sin, cos and tan using your calculator.
Here are some solved examples to study ( and practice) for using your calculator to find sin, cos and tan.
1. Use your calculator to find the following values. ( round to the nearest thousandth)
a. sin 56o = 0.829
b. cos 32o = 0.484
c. tan 71o= 2.904
d. sin 22o = 0.375
e. cos 61o = 0.485
f. tan 29o = 0.554
 Self-Check
Self-Check
Complete the following self check using the link below to check your work.
1. Find the sin, cos and tan for the acute angles. Write your answer in both fractional and decimal form ( round the decimal form to the nearest thousandth).
a.
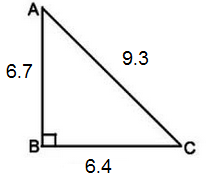
b. 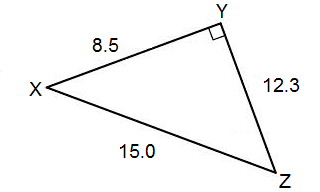
2. Use your calculator to find the following answers. Round to the nearest thousandth. ( Make sure your calculator is in degree mode).
a. sin 35o
b. cos 17o
c. tan 49o
d. sin 68o
e. cos 84o
f. tan 26o