Lesson 2
1. Lesson 2
1.1. Discover
Module 1: Trigonometry
Discover
In Lesson 1 you used the Pythagorean theorem and the primary trigonometric ratios to solve problems involving triangles. Since you only used these formulas for right triangles, you should investigate if they are valid for oblique triangles.
Try This 1
You should place your completed Try This activities in your course folder. Your teacher may ask to see your completed Try This activities.
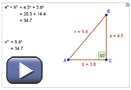
Use the Pythagorean Theorem Explorer applet to investigate the types of triangles where a2 + b2 = c2 is valid and where it is not valid. As you drag the points, you will see how the different pieces of the Pythagorean theorem relate to each other.
Think about the following questions while you use the Pythagorean Theorem Explorer:
- What types of triangles make a2 + b2 = c2?
- What types of triangles make a2 + b2 ≠ c2?
- What do a, b, and c in the Pythagorean theorem represent?
Share 1
Compare your conclusions with a partner. With your partner, answer the following questions:
- What types of triangles make a2 + b2 = c2?
- What types of triangles make a2 + b2 ≠ c2?
- The letters in the Pythagorean theorem represent specific sides in a triangle. Which one side (a, b, or c) gives you a hint that the formula may not be valid for all triangles? Explain why.
![]() Place a copy of your conclusions in your course folder.
Place a copy of your conclusions in your course folder.