Module 7
Completion requirements
Created by IMSreader
1. Module 7
1.12. Page 2
Module 7: Trigonometry
Get Started
In this example you will review the names of the sides of a right triangle relative to one of its acute angles. When an acute angle is specified in a right triangle, the acute angle is referred to as the reference angle.
Example 1
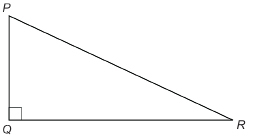
- Label the sides of ΔPQR using the letters p, q, and r.
- In relation to ∠R, which side is the side opposite? Which is the side adjacent? Which is the hypotenuse?
- In relation to ∠P, which side is the side opposite? Which is the side adjacent? Which is the hypotenuse?
- Regardless of which acute angle is the reference angle, which side always has the same name or label?
Solution
-
Side p is across from ∠P. Side r is across from ∠R. Side q is across from ∠Q.
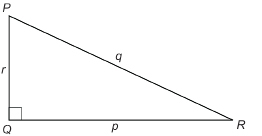
-
In relation to ∠R, side r is the side opposite, side p is the side adjacent, and side q is the hypotenuse.
-
In relation to ∠P, side p is the side opposite, side r is the side adjacent, and side q is the hypotenuse.
-
Side q, the longest side, is always the hypotenuse.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
Try these questions. Use the following diagram.
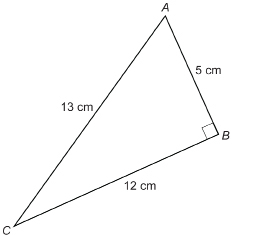
SC 1. What single letter could be used to name side AC? Side BC? Side AB?
SC 2. What is the length of the side opposite ∠A? The side adjacent to ∠A?
SC 3. What is the length of the side opposite ∠C? The side adjacent to ∠C?
SC 4. What is the length of the hypotenuse?