Module 8
1. Module 8
1.22. Page 5
Module 8: Daily Living
Shift Differential
Workers on wages may be paid extra for working Sundays or holidays. Depending on the working agreement, in some instances the wage could be paid at double-time, or the worker could receive time off in the future as compensation—time in lieu.
shift differential: a bonus paid to compensate workers taking an undesirable shift
In shift work, there may be bonuses paid to work the less-desirable shifts. For instance, a worker might be paid a 20% bonus for working the night shift. This bonus is called a shift differential.
Example 5
Morris works at a convenience store. On a regular shift, he is paid $12.00/h. When he works the night shift, he is paid a shift differential of 20%. What are his hourly wages on the night shift?
Solution
Method 1
Morris’s regular wages are $12.00/h. The night-shift bonus is 20%. So the hourly rate at night will be 100% + 20% = 120% of his regular wage.
120% = 1.20
120% of $12.00 = $14.40
$12.00 × 1.2 = $14.40
Morris’s wage at night is $14.40/h.
Method 2
Find the shift differential in dollars per hour. The bonus is 20%.
![]()
Morris receives an extra $2.40/h at night.
![]()
 Self-Check
Self-Check
In the next question you will calculate the shift differential as a percent.
SC 7. Anuka’s wage when he works the day shift is $15.00/h. When he works the evening shift, he earns $15.60/h. What is the shift differential as a percent?
Salaries
salary: a set amount paid to an employee for the performance of regular duties of a position over a period of one year (or other specified period of time)
To this point in Lesson 4, you have explored wages. Some employees, such as most clerical workers, managers, accountants, bankers, teachers, firefighters, clergy, and police officers, are not paid wages. Instead, these employees earn salaries.
An electrical engineer, for example, might sign a contract to work for a firm for an annual salary of $84 000. Of course, she would not be paid a lump sum; she would be paid monthly. Her monthly salary would $84 000 ÷ 12 months, or $7000 every month.
Did You Know?
In 2007, the average annual income for a family with two working parents was $77 300.
Employers prefer to pay their management, clerical, and professional staff salaries, as they know what the cost of each employee will be over the year. This is not the case with workers on wages; for wage employees, time on the job and overtime are difficult to predict.
Salaried employees often receive benefits, contribute to pension funds, and take fixed-length holidays that are not always available to workers on wages. And, unlike hourly workers, salaried workers generally do not have to punch a time clock. Unlike workers on wages, salaried employees know exactly how much they are going to earn each month, so it is easier for them to budget.
Salaried workers are not paid overtime for performing their regular duties. For example, school teachers, who are on a salary, are not paid overtime for planning and marking exams and assignments. Although this work may have to be done outside of standard work hours, it is simply considered part of the job.
Example 6
Kathy works as a dietitian in Whitehorse. She is a salaried employee. Her salary before deductions is $7240.00/mo.
- What is Kathy’s annual salary?
- Kathy’s employer says she will receive a 4% raise in January. What will Kathy’s annual salary be after the raise?
Solution
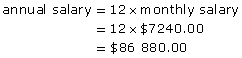
- With a 4% raise, Kathy will earn 100% + 4% = 104% of her present salary.
104% = 1.04
1.04 × $86 880.00 = $90 355.20
So, 104% of $86 880.00 is $90 355.20.
Next January, Kathy’s annual salary will be $90 355.20.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
In the next set of questions you will make decisions based on your knowledge of salaries and wages.
SC 8. Mary-Ellen is a plumber. She works for an hourly wage. Over the course of the year, she has worked for several different employers and at several different job sites. Last month, with regular wages and overtime, Mary-Ellen earned $6300.00. Can you predict Mary-Ellen’s annual income?
SC 9. Marty is an office-staff employee at the local Band Office. If his monthly salary is $4500.00, what is Marty’s annual salary?
When Does the Paycheque Arrive?
biweekly: every two weeks
semimonthly: twice a month
Businesses often pay their salaried workers monthly. However, some workers are paid biweekly or semimonthly.
For a worker who is paid biweekly, because there are 52 weeks in a year, there would be 52 ÷ 2, or 26, pay periods in the year.
For a worker who is paid semimonthly, because there are 12 months in a year, there would be 12 × 2, or 24, pay periods in the year.
You may have noticed that hourly wages are also unit rates ($/h). Salaries are also a unit rate ($/yr). With salaries, the unit could be changed and different unit rates calculated depending on whether the salary is paid biweekly ($/wk) or semimonthly ($/mo). The following Mastering Concepts question explores this concept.
 Mastering Concepts
Mastering Concepts
Jody has been hired as an office assistant at the local school. Her annual salary is $36 000.00. What would Jody’s salary be each pay period if she were paid as follows?
- monthly
- semimonthly
- biweekly