Lesson 1
1. Lesson 1
1.5. Explore
Module 4: The Right Kind Of Triangles
Explore
The Pythagorean theorem states that for any right triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the two legs.
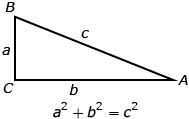
In this section you will apply the Pythagorean theorem in a variety of practical situations.
First, to be able to identify right-angled triangles in any context is important. Watch the video, Exploring the Pythagorean Theorem, and then answer the question that follows.
Share 2
Share three examples of right-angle triangles from real life with a partner or group. Think of examples not described in the video.
Try This 2

iStockphoto/Thinkstock
Carpenters use ladders on a regular basis. For safety, the foot of a ladder should be 1 ft away from the wall for every 4 ft up the wall the ladder reaches.
- Sketch the position of a ladder that reaches 4 ft up the wall. Include all measurements.
- To reach 12 ft up a wall, how far away from the wall must the foot of the latter ladder be positioned?

- Sketch a diagram showing the safe use of a ladder that reaches 12 ft up a wall. Identify the right triangle. Indicate the known measurements.
- In order to use a ladder safely, calculate the length of ladder required to reach 12 ft up a wall. Round your answer to one decimal place.
- What is the slope of this ladder? Will the slope be negative or positive?

![]() Save your responses to your course folder.
Save your responses to your course folder.
![]()
