Section 2
Completion requirements
Created by IMSreader
1. Section 2
1.18. Explore 3
Section 2: Perspective and Scale
Try This 3
Sometimes on a map, instead of a ratio such as 1:125 000, the scale is expressed as 1 cm = 1.25 km. If this is the case, think about how this data might change the calculation.
- Set up the proportion you would use. Check

- Solve the proportion to find the actual distance. Check

Scale is used on maps, blueprints, mechanical drawings, microscopic diagrams, model planes and trains, and photography. Now that you have been introduced to scale, it’s time for you to draw scale diagrams of some everyday two- and three-dimensional objects.

Comstock/Thinkstock
Example
An antique trunk is 40 cm wide, 100 cm long, and 60 cm high. Draw a scale diagram of this trunk on 1-cm isometric paper.
Solution
The trunk is 40 cm wide, 100 cm long, and 60 cm high.
- Choose a scale.
- If 1 cm on the isometric paper is equal to 10 cm for the actual trunk, the scale is 1:10.
- If 1 cm on the isometric paper is equal to 10 cm for the actual trunk, the scale is 1:10.
- Set up proportions using the scale 1:10 to find the length of each side in the scale drawing.
- Width of trunk in scale drawing:
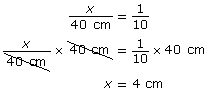
- Length of scale diagram = 100 cm ÷ 10 = 10 cm.
- Height of scale diagram = 60 cm ÷ 10 = 6 cm.
- Width of trunk in scale drawing:
-
Draw the 3-D isometric image.
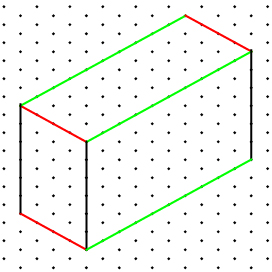
- Draw the height (shown in black) 6 cm high. This will be one corner of the box.
- Draw the width (shown in red) 4 cm long.
- Draw the length (shown in green) 10 cm long.
- Then complete the 3-D image of the trunk.
- Draw the height (shown in black) 6 cm high. This will be one corner of the box.
