Lesson 2
1. Lesson 2
1.6. Explore 2
Module 6: Surface Area

Jack Hollingsworth/ Photodisc/Thinkstock
In Try This 2 you estimated the size of the toonie three different ways—using grid paper, using a referent, and taking rough measurements. In the next example you will see how Jenn used a referent to estimate the surface area of her front door.
Example 1
Jenn used her referent of a square metre (1 m2) to estimate the total surface area of the front door in her home. She made sure to measure all six surfaces (the front, the back, and the four edges) to get the best estimation possible.
She estimated the surface area of the door to be about 4 m2.
Jenn then decided to check her estimation skills. She took careful measurements with a measuring tape and drew a net to record the measurements. She then calculated the door’s surface area in order to see how close her estimate was to the actual area.
Jenn’s door measured 0.91 m wide, 2.03 m tall, and 4.5 cm or 0.045 m thick. Her sketch of the net of the door looked like this.
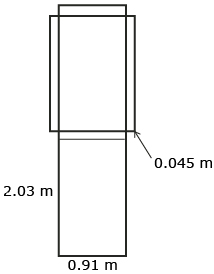
Jenn then calculated the surface area of the door using the steps below.
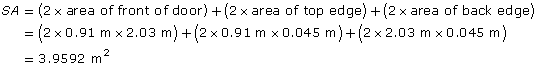
Jenn was happy to see that her estimate of 4 m2 is very close to the actual area.
In the last example, Jenn used a referent to do her estimation of the surface area of the door. In the next example, referents and rounding are both used in the estimation.