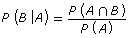Lesson 3
1. Lesson 3
1.8. Explore 7
Module 2: Probability

Jupiterimages/Comstock/Thinkstock
Sometimes predictions are made that involve dependent events. In board games, for example, one player’s move depends on what an opponent has done. A player might have a next move all planned out, but an opponent can foil those plans with a preceding move!
Read “Example 4” on page 186 of your textbook, and review Hillary’s solution to see how different possibilities are considered when predicting the probability of Hillary’s team winning.
Self-Check 5
- Complete “Your Turn” on page 187 of your textbook. Answer
- Complete question 6 on page 189 of your textbook. Answer
Being able to differentiate between independent and dependent events can sometimes be challenging. In the next Self-Check, you will need to identify if the events are independent or dependent before solving the problems. Using a graphic organizer, such as a chart, a tree diagram, or a Venn diagram, can be helpful to sort necessary information.
Self-Check 6
- Open the Compound Independent and Dependent Events gizmo, and complete the five “Assessment Questions” that follow the simulation. Press “Check Your Answers” to ensure you have fully understood the questions.
![]()
- Complete question 2 on page 198 of your textbook. Answer
- For Company X, expected sales are based on the strength of the economy and past statistics. For 34% of the time in a good economy, the expected sales would be $10 million. The company predicts that there is a 54% chance of a good economy this year. Determine the probability that the expected sales will be $10 million. Answer
- Complete question 11 on page 199 of your textbook. Answer
- Complete question 18 on page 201 of your textbook. Answer
Add the following terms to your copy of Glossary Terms:
- independent events
- dependent events
- conditional events
Add the following formulas to your copy of Formula Sheet:
- independent events: P(A ∩ B) = P(A) × P(B)
- dependent events: P(A ∩ B) = P(A) × P(B|A) or