Lesson 5
1. Lesson 5
1.5. Explore
Module 3: Permutations, Combinations, and the Fundamental Counting Principle
Explore

Jupiterimages/ Polka Dot
/Thinkstock
In Try This 1, you may have found that using the fundamental counting principle and permutations helped to simplify probability calculations. There are many situations where this is the case.
Suppose you have a library of 10 country and 17 rock songs on an MP3 player. If 5 songs are picked at random, what is the probability of making a 5-song playlist with only rock music?
In this example, a favourable outcome is a playlist with 5 rock songs. The total outcomes are all the possible 5-song playlists. If you change the order of songs, you get a different playlist. Order is important, so use permutations.
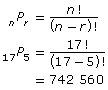 |
Determine the number of 5-song playlists containing only rock songs. In the equation, n is the total number of rock songs, and r is the number of rock songs. |
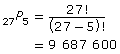 |
Determine the total number of 5-song playlists possible. In the equation, n is the total number of songs, and r is the number of songs in the playlist. |
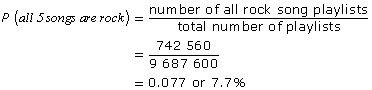 |
Determine the probability of the 5-song playlist containing 5 rock songs. |
Depending on the scenario, combinations may also prove useful when determining probabilities. You may also need to use the probability rules for the words and and or that you learned in Module 2.
Try This 2

Ryan McVay/Digital Vision/Thinkstock
Using the playlist example as a guide, solve the following problems.
A winter carnival committee of 6 people needs to be selected from 8 boys and 10 girls.
- Complete the following to determine the probability that the committee will have 3 boys and 3 girls.
- Is order important for this problem? Explain.
- Determine the number of favourable outcomes. This is the number of ways of choosing 3 boys from 8 boys and 3 girls from 10 girls.
- Determine the number of total outcomes. This is the number of ways of choosing 6 people from 18 people.
- Determine the probability of 3 boys and 3 girls by dividing the number of favourable outcomes by the total number of outcomes.
-
- What information will be required to calculate the probability that at least 2 members are girls?
- Calculate the probability that at least 2 members are girls.
- What information will be required to calculate the probability that at least 2 members are girls?
![]() Save your responses in your course folder.
Save your responses in your course folder.