Module 4 Intro
1. Module 4 Intro
1.7. Page 5
Module 4—Properties of Solutions
 Read
Read
Read the section “Properties of Aqueous Solutions” on pages 193 and 194 in your textbook to learn more about the test for conductivity and the properties of acidic, basic, and neutral solutions.
The Aqueous Phase
As you read in the previous section, drinking water can contain many dissolved substances. Not only can dissolved substances provide colour or taste, but they can make a solution have other unique properties.
aqueous phase: a phase denoting a highly soluble substance that has been dissolved in water; denoted by (aq)
conductivity: the ability of a solution to transfer an electric current
electrolyte: a solution that conducts an electric current
nonelectrolyte: a solution that does not conduct an electric current
If sugar is dissolved in water, can it still it be written as C12H22O11(s)? The answer to this question is no, since the sugar molecules are no longer behaving as a crystalline solid—they are dispersed throughout the solution. The aqueous phase (aq) is used to indicate that a substance is dissolved in water. Note that a solute is said to be aqueous only if it is dissolved in water. If it is dissolved in a different solvent, such as alcohol, the phase would be written (alc).
Two other properties often considered when investigating solutions are conductivity and acidity. (Solubility is another property, which will be addressed in a later lesson.)
Some solutions demonstrate conductivity. A solution that conducts electricity contains electrolytes. Electrolytes are charged ions present within a solution. Their ability to move allows a current to be established within a solution. Tap water conducts electricity because the ions of dissolved solutes are present, while pure distilled water would not conduct electricity since no ions are present. Many molecular compounds form solutions that are nonelectrolytes because the solute does not form ions when it dissolves. Therefore, solutions containing dissolved molecular compounds do not conduct electricity.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
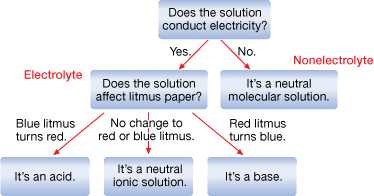
SC 3. Examine the diagram below. Identify where an electrolyte and nonelectrolyte would appear on the chart.
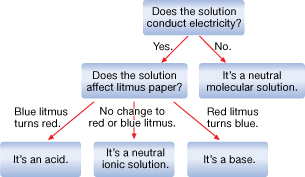
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 3.