Module 4 Intro
1. Module 4 Intro
1.39. Page 5
Module 4—Properties of Solutions
 Read
Read
Ion Concentrations
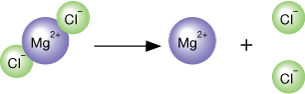
Recall from previous lessons that many substances dissociate in water to form ions. It is possible to calculate the concentration of these ions using amount concentrations and a balanced chemical formula. Read “Concentration of Ions” on pages 210 and 211 in your textbook for more information on the effect dissociation has on the ion concentration in a solution. Then work through “COMMUNICATION examples” 12, 13, and 14 on pages 211 and 212.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 8. Determine the amount concentration of calcium ions and acetate ions in a 0.81-mol/L solution of calcium acetate.
SC 9. Determine the amount concentration of the sodium ions and carbonate ions in a 0.65-mol/L solution of sodium carbonate.
SC 10. Determine the amount concentration of the ammonium ions and the phosphate ions in a 1.15-mol/L solution of ammonium phosphate.
SC 11. Determine the amount concentration of potassium ions and dichromate ions in a solution made by dissolving 42.5 g of potassium dichromate to make a volume of 160 mL.
SC 12. What mass of aluminium chloride must be dissolved to make 52 L of solution with a chloride-ion concentration of 0.45 mol/L?