Module 2
1. Module 2
1.5. Page 3
Module 2—The Conservation of Momentum in Isolated Systems
 Lesson 1 Lab: Elastic Collisions Lab
Lesson 1 Lab: Elastic Collisions Lab
Problem
Is momentum conserved in a linear collision?
Procedure
-
Perform five different collisions using the Collision 1D simulator, and complete the data tables in Observations.
-
For clarity on the simulator, toggle “Show CM” and “Show CM Frame” to the off position (
 ).
).
-
To generate a new collision, click the “New” button (
 ) and change the initial velocity of the blue ball by adjusting the velocity slider (
) and change the initial velocity of the blue ball by adjusting the velocity slider ( ) to any value.
) to any value.
-
After each collision, view the collision information by clicking the “Data” button (
 ) and fill in the appropriate table.
) and fill in the appropriate table.
-
The following equations will be required to complete the tables:
 and
and 
Observations
Collision 1 (Sample Data) |
||||||||||||
Object |
mass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
blue |
4.0 |
+8.0 |
−0.86 |
−8.86 |
+32 |
−3.44 |
−35.44 |
|||||
green |
9.0 |
0 |
+3.94 |
+3.94 |
0 |
+35.46 |
+35.46 |
|||||
Collision 2 |
||||||||||||
Object |
mass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
blue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
green |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Collision 3 |
||||||||||||
Object |
mass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
blue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
green |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Collision 4 |
||||||||||||
Object |
mass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
blue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
green |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Collision 5 |
||||||||||||
Object |
mass |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
blue |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
green |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
 Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment
Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment
Remember to submit the answers to LAB 1, LAB 2, and LAB 3 to your teacher as part of your Module 2: Lesson 1 Assignment.
Analysis
LAB 1.
-
Is there a relationship between the changes in velocity of the blue mass and the green mass? If yes, describe the relationship.
-
Is there a relationship between the changes in momentum of the blue mass and the green mass? If yes, describe the relationship.
You should see an interesting connection between the changes in momentum of each mass: the changes in momentum should be equal, but opposite. For example, if the blue mass has an increase in momentum, then the green mass has a decrease in momentum by the same amount. This connection leads us to an important concept about momentum and what happens to the total momentum of a system in a collision.
LAB 2. If the change in momentum of one object is exactly equal but opposite to the change in momentum of another object, what does that indicate about the total momentum of the system?
LAB 3. If the total momentum of a system before a collision is equal to the total momentum of a system after a collision, then momentum is conserved. For each of the five collisions, verify that the total initial momentum is equal to the total final momentum by completing the following table.
Notice the following shorthand way of talking about the sum of the momentums of the blue and green masses. The capital Greek letter sigma (Σ) is often used to denote sums.
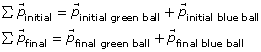
Collision |
Total Initial
(kg·m/s) |
Total Final (kg·m/s) |
Is Momentum Conserved? |
1 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
Based on the lab activity, you should have found that the total momentum is conserved in a collision within an isolated system.