Module 2
1. Module 2
1.14. Page 5
Module 2—The Conservation of Momentum in Isolated Systems
 Read
Read
Read “Inelastic Collisions” on page 483 of your physics textbook. Continue by studying “Example 9.10” on pages 484 and 485 of your textbook.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 4. Answer “Practice Problem 1” on page 484 of your textbook.
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 4.
Given
![]() mp = 1.00 kg
mp = 1.00 kg ![]()
Required
The velocity of the bullet just before impact, ![]() .
.
Analysis and Solution
Choose the system of bullet and pendulum as an isolated system. Since the pendulum is stationary before the bullet hits, its initial velocity is zero; thus, its initial momentum ![]() . After the collision, the bullet and pendulum move together as a unit. The kinetic energy of the pendulum-bullet system is converted into gravitational potential energy:
. After the collision, the bullet and pendulum move together as a unit. The kinetic energy of the pendulum-bullet system is converted into gravitational potential energy:
Ek = Ep
Apply the law of conservation of energy to find the speed of the pendulum-bullet system just after impact:
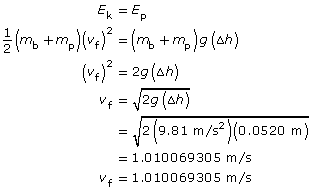
Apply the law of conservation of momentum to find the initial velocity of the bullet:
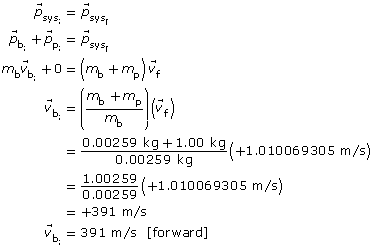
Paraphrase
The initial velocity of the bullet immediately before impact was 391 m/s [forward].
 Read
Read
Study “Example 9.11” on page 485 of your textbook.
 Self-Check
Self-Check
SC 5. Answer “Practice Problem 1” on page 485 of your textbook.
 Self-Check Answers
Self-Check Answers
SC 5.
Given
mass of dart md = 0.012 kg
mass of block-glider mb = 0.200 kg
final velocity of system ![]()
initial velocity of dart ![]()
Required
The amount of kinetic energy lost immediately after the interaction.
Analysis and Solution
the initial energy of the system comes from the kinetic energy of the dart:
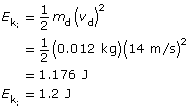
The final kinetic energy comes from the dart-block-glider system.
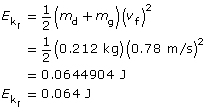
The difference between the initial and final kinetic energies is the kinetic energy lost.
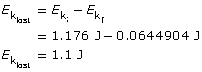
Paraphrase
There was 1.1 J lost immediately after the interaction of the dart and the block-glider system.
 Try This
Try This
TR 1. Answer “Practice Problem 2” on page 484 of your textbook.
TR 2. Answer “Practice Problem 2” on page 485 of your textbook.
 Module 2: Lesson 2 Assignment
Module 2: Lesson 2 Assignment
Remember to submit the answers to A 3 to your teacher as part of your Module 2: Lesson 2 Assignment.
A 3. Design an experiment that would let you answer the following problem:
Is the collision between a ball pendulum and a block pendulum elastic, inelastic, or completely inelastic?
The following four diagrams give you a starting point for your experiment.
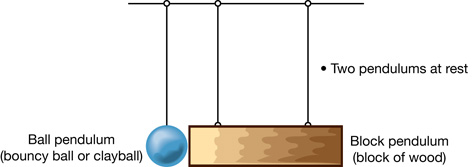
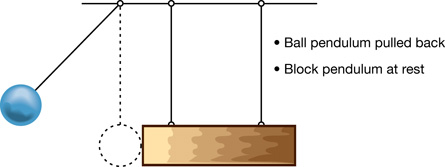
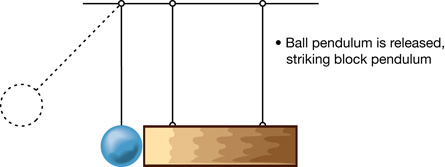
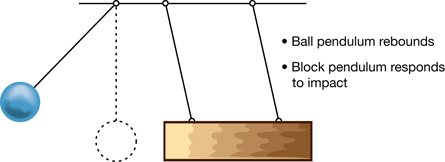
From “Examples 9.10” and “9.11” of your textbook, you will be familiar with using gravitational potential energy to find the kinetic energy of a ball pendulum. You can deal with the kinetic energy of the block pendulum in a similar fashion.
You need to present the following in your experimental design:
-
the measurements that need to be taken
-
the calculations that would have to be made
-
the criteria you would use to answer the problem