Module 3
1. Module 3
1.37. Page 8
Module 3—Electrical Phenomena
 Lesson 5 Lab: Storing Energy in Uniform Electric Fields
Lesson 5 Lab: Storing Energy in Uniform Electric Fields
Purpose
In this lab activity you will use a computer simulation to collect data enabling you to answer the following questions:
- How does a test charge move in a uniform electric field?
- How can this motion be explained using physics principles?
Procedure
Step 1: You may be required to enter a username and password. Contact your teacher for this information. Open the Electric Field Potential, Uniform simulation, and enter the following settings:
- Reset the simulation (
 ). Note that in this simulation the electric field is not varying as it is in the region surrounding a single point charge. The electric field in this simulation is uniform in strength and direction once the “play” button (
). Note that in this simulation the electric field is not varying as it is in the region surrounding a single point charge. The electric field in this simulation is uniform in strength and direction once the “play” button ( ) is pressed.
) is pressed.
- Turn on the grid (
 ).
).
- Click on the “mode” button (
 ) for both the electric field and velocity until both of these quantities are displayed in the polar method (
) for both the electric field and velocity until both of these quantities are displayed in the polar method ( ), showing a direction in degrees.
), showing a direction in degrees.
- Enter the following values for the electric field: 10.0 V/m at 0°. (Note that the unit for field used here, the volt per metre, is equivalent to a newton per coulomb. You’ll learn more about this later in the lesson.)
- Click on the vectors button, and turn on the electric field vector from the “Visible Vectors” option box.
- Enter the following values for the initial velocity: 5.0 m/s at 0°.
- Drag the test charge (red dot) to the following location: (x,y) = (100,0).
- Click on the “initial position” button (
 ) to have this position be the point where initial values are determined.
) to have this position be the point where initial values are determined.
- If you choose to rewind (
 ), you can return to these initial settings at any time during this lab activity. However, if you use the “reset” button (
), you can return to these initial settings at any time during this lab activity. However, if you use the “reset” button ( ), you would have to re-enter all these initial settings.
), you would have to re-enter all these initial settings.
If these settings have been applied, the screen should look like these settings.
Step 2: For the Analysis, you will need to collect the following data from the screen:
![]() = __________
= __________ ![]() = ____________
= ____________
qtest = ___________ mtest = _____________
Step 3: Press play (![]() ), and observe the motion of the test charge until it reaches the point (x,y) = (300,0). Then press the “pause” button (
), and observe the motion of the test charge until it reaches the point (x,y) = (300,0). Then press the “pause” button (![]() ). Use “rewind” (
). Use “rewind” (![]() ) if it takes several attempts to get this right. Record the final velocity for the particle once it has reached (300,0). You will use this value for the Analysis.
) if it takes several attempts to get this right. Record the final velocity for the particle once it has reached (300,0). You will use this value for the Analysis.
![]() = ___________
= ___________
Analysis
 Self Check
Self Check
SC 12.
- Calculate the magnitude and direction of the electrostatic force acting on the test charge at the locations (100,0) and (300,0).
- Draw a free-body diagram to show the force acting on the particle at the points (100,0) and (300,0).
- Refer to your answer to SC 12.b. How is this free-body diagram different from the one that you drew in the previous lab activity when the electric field was non-uniform?
- Use your values for electrostatic force to calculate the acceleration of the test charge at the locations (100,0) and (300,0).
 Self Check Answers
Self Check Answers
SC 12.
a.
Given
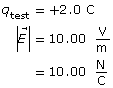
Required
The magnitude and direction of the electrostatic force at 100 m and 300 m, ![]()
Analysis and Solution
- The electric field is directed from left to right, so the electrostatic force acting on a positive test charge will also be from left to right.
- The electric field has the same magnitude in both locations, so the magnitude of the electrostatic force will be the same in both locations for a given test charge.
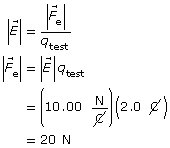
Paraphrase
The electrostatic force will be 20 N [right] in both locations.
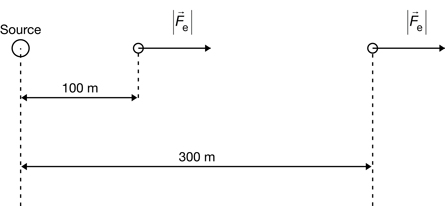
- When the electric field is uniform, the electrostatic force vectors have the same magnitude and direction in all locations. This stands in contrast to the situation in the previous lab activity where the electrostatic force vectors decreased in magnitude as the distance increased from the source.
Given
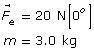
Required
The acceleration of the test charge at 100 m and at 300 m.
Analysis and Solution
The acceleration will be the same at both locations because the electrostatic force is the same at each location.
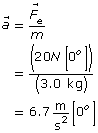
Paraphrase
The acceleration of the text charge is 6.7 m/s2 [0°] at both 100 m and 300 m.
Conclusion
 Module 3: Lesson 5 Assignment
Module 3: Lesson 5 Assignment
Remember to submit the answer to LAB 7 to your teacher as part of your Module 3: Lesson 5 Assignment.
LAB 7. Describe the motion of a test charge in a uniform electric field.
LAB 8. Explain the motion of a test charge in a uniform electric field.
LAB 9. Explain why the equation ![]() cannot be applied in this situation.
cannot be applied in this situation.