Lesson 4
1. Lesson 4
1.9. Explore 5
Module 5: Geometry
A dilation is the enlargement or reduction of a figure around a fixed point.
Source: MathWorks 12 Student Book/Teacher Guide. (Vancouver: Pacific Educational Press, 2011.)
Dilations are the next type of transformation you will focus on. A dilation is the enlargement or reduction of a figure around a fixed point. In this course you will use the point (0, 0) as the centre of dilation. Dilations are useful if you have an object and you would like to produce a similar object but of a different size.
Try This 4
The following images show a polygon and two dilations. The first dilation is 0.5 times the size of the original polygon and the second dilation is 2 times the size of the original polygon.
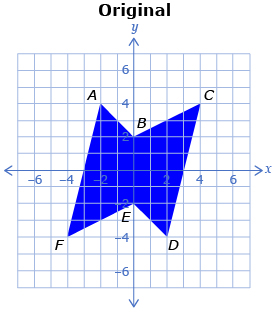
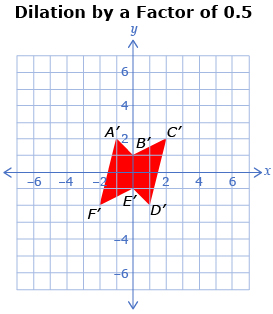
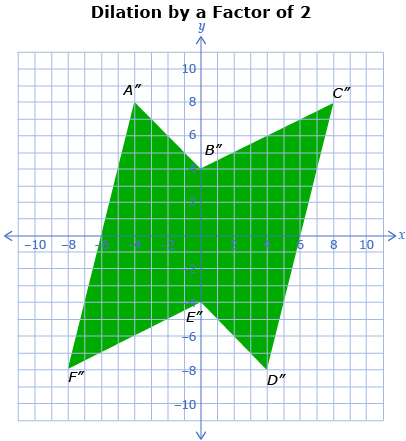
-
- Describe how the three polygons are related.
- Complete a table like the one shown.
Point on Original
Corresponding Point on Dilation by a Factor of 0.5
Corresponding Point on Dilation by a Factor 2
A(−2, 4)
A′(−1, 2)
A″(−4, 8)
B(0, 2)
C(4, 4)
D(2, −4)
E(0, −2)
F(−4, −4)
- Describe how the corresponding points are related to the original points.
- Predict a rule that will determine the points of an object 3 times the size of the original.
- Predict a rule that will determine the points of an object 0.6 times the size of the original.
- How can you decide if the dilation will result in a larger figure or a smaller figure?
- Continue exploring dilations by opening Dilations.

- Pick a point on the shape you would like to work with. (You can change the shape of the polygon by moving the vertices. If you do this, keep the size of your shape similar to the size of the original shape.)
- Use the rule you predicted in 1.c. to determine where your point will be after a dilation by a factor of 3.
- Use the rule you predicted in 1.d. to determine where your point will be after a dilation by a factor of 0.6.
- Enter the dilation factors 3 and 0.6 into the input box in the Dilations interactive to check your answers to 2.b. and 2.c.
![]() Save your responses in your course folder.
Save your responses in your course folder.