Lesson 1
1. Lesson 1
1.9. Explore 5
Module 4: Polynomials
In End Behaviour Explorer that you used to complete Try This 3, you may have found that only the leading coefficient, the a-value, affected the end behaviour. You should have also discovered that the end behaviour only changed if the sign of the leading coefficient changed.
The sign of the leading coefficient predicts end behaviour.
Cubic |
y = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d |
Quadratic |
y = ax2 + bx + c |
Linear |
y = ax + b |
Constant |
y = a |
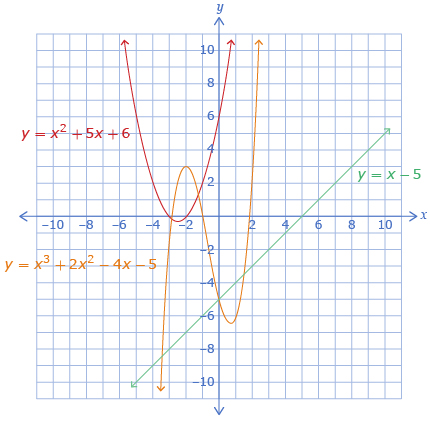
Functions with a positive leading coefficient end in quadrant I. Functions with an even degree and positive leading coefficient begin in quadrant II, and functions with an odd degree and positive leading coefficient begin in quadrant III.
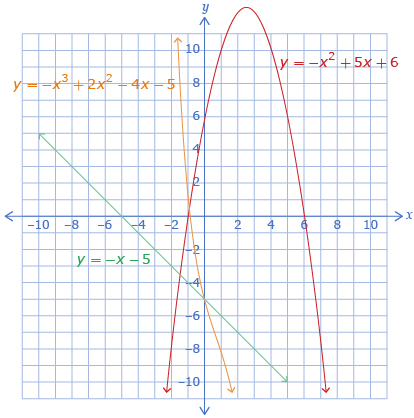
Functions with a negative leading coefficient end in quadrant IV. Functions with an even degree and negative leading coefficient begin in quadrant III, and functions with an odd degree and negative leading coefficient begin in quadrant II.
In Try This 3 you may have also found that the y-intercept has the same value as the constant term.
The value of the constant term predicts the y-intercept.
Cubic |
y = ax3 + bx2 + cx + d |
Quadratic |
y = ax2 + bx + c |
Linear |
y = ax + b |
Constant |
y = a |
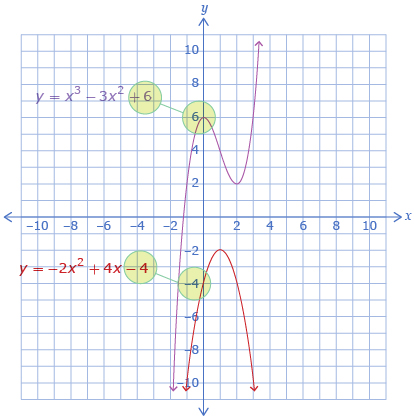
The y-intercept is equal to the constant term for all polynomials.